Fundamental Design Elements of Tapered Rolling Bearings
Tapered Geometry: The Core of Performance
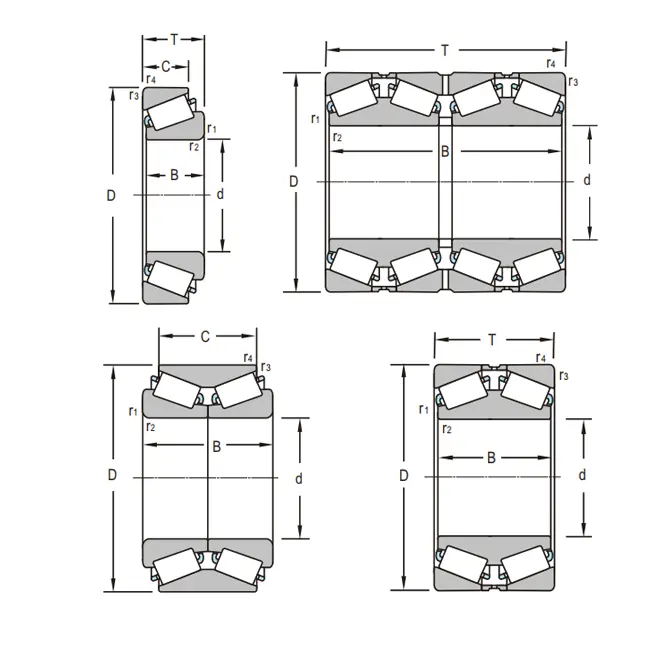
The distinctive geometry of tapered rolling bearings is its distinguishing feature. The inner ring, also referred to as the cone, has a tapered raceway that matches the taper of the outer ring (or cup). The bearing can effectively manage both radial and axial stresses at the same time thanks to its design, which establishes a precise angle of contact between the rollers and raceways. In order to maximize load distribution and reduce friction, the taper angle is meticulously computed, leading to improved durability and performance.
To meet the needs of a certain application, engineers might adjust the taper angle. More axial load capacity is often offered by steeper angles, and better radial load management is provided by shallower angles. This adaptability enables modification for a broad variety of industrial requirements, from slow-moving, heavy-load mining and construction equipment to high-speed automobile applications.
Roller Design: Precision-Engineered for Optimal Contact
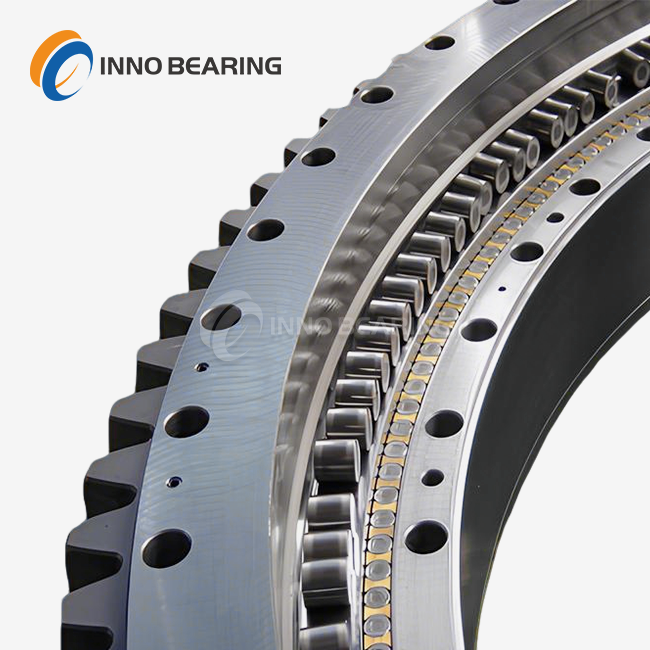
Tapered bearings use properly designed conical rollers rather than basic cylinders. The load-bearing surface area is maximized by their geometry, which makes line contact with the inner and outer raceways. Compared to ball bearings, which use point contact, this line contact distributes the load more uniformly, enabling tapered roller bearings to support much larger loads.
Roller profiles may be made with extreme precision thanks to advanced manufacturing capabilities. To further improve durability, some designs include a little amount of crowning or profiling at the rollers' ends to avoid edge stress concentrations. Important design considerations also include the size and quantity of rollers; bigger rollers often have a better load capacity, but this may come at the expense of increased friction and heat production.
Cage Design: Ensuring Proper Roller Spacing and Guidance
Maintaining appropriate roller spacing and directing the rollers during rotation are critical functions of the cage, also known as the retainer. Because the rollers are tilted in tapered roller bearings, the cage design is very crucial. Roller skewing and misalignment may be avoided using high-quality cages that are designed to reduce friction and provide strong support.
The materials used for cages might change according on the use. Stamped steel cages are common in many industrial applications due to their strength and cost-effectiveness. Machined brass cages may be the better option for high-speed or high-temperature settings due to their better heat-dissipating capabilities. When it comes to weight reduction and longer maintenance intervals, polymer cages with incorporated lubricants may provide special benefits.

Advanced Features for Enhanced Performance
Separable Components: Simplifying Assembly and Maintenance
The detachable design of tapered roller bearings is one of its main benefits. It is possible to install the inner ring (cone) with its cage and rollers independently of the outer ring (cup). Especially in complicated equipment where access may be restricted, this feature significantly streamlines the installation and disassembly procedure. Additionally, it makes individual component inspection and maintenance simpler, which might increase the bearing assembly's total lifetime.
This separability extends to enabling modification of bearing preload or clearance in some types, especially double-row tapered roller bearings. Engineers may optimize load capacity and rotational accuracy by fine-tuning the bearing's performance characteristics to fit particular operating circumstances by varying the axial position of one row relative to the other.
Sealing Solutions: Protecting Against Contamination
Advanced sealing techniques have been developed to guard against pollutants in hostile environments, even though many tapered roller bearings have open designs. These might be anything from simple contact sealing to intricate labyrinth patterns that give possible pollutants a convoluted route. Certain high-performance bearings include many sealing components, such as metal shields or labyrinth structures combined with rubber lip seals.
Innovative sealing Solutions improve service intervals and save maintenance costs by keeping lubrication within the bearing and preventing impurities from entering. Specialized seals may be used for applications in very difficult settings, such mining or food processing, in order to withstand chemical assault or satisfy strict hygienic requirements.
Material Innovations: Pushing the Boundaries of Performance
The performance and longevity of tapered roller bearings may be greatly impacted by the materials used. Because of its exceptional hardness and resistance to wear, traditional high-carbon chromium steel (such as GCr15 or 100Cr6) is still a preferred option for many applications. However, more specific alloys could be used in harsher environments.
For applications requiring severe shock loads, case-hardened steels such as 20Cr2Ni4A provide a mix of hard surface and robust core. Stainless steel versions provide better protection in corrosive conditions. Materials like M50 tool steel or even ceramic hybrid bearings push the operating boundaries of conventional bearings in high-temperature applications. In situations that were previously thought to be too demanding for rolling element bearings, these material innovations enable tapered roller bearings to operate dependably.

Optimizing Tapered Rolling Bearings for Specific Applications
Precision Engineering for High-Speed Applications
The design of tapered roller bearings requires careful attention to detail in high-speed applications like machine tool spindles or automobile gearboxes. In order to retain exact geometry under dynamic loads, engineers concentrate on reducing heat production and friction. This often entails using cutting-edge cage designs that encourage effective lubrication flow and improving the roller end profile to lessen edge stress.
When it comes to high-speed performance, surface coatings are essential. By achieving surface roughness levels as low as Ra ≤0.1μm, super-finishing processes may drastically reduce wear and friction. Furthermore, certain coatings such as diamond-like carbon (DLC) may improve tribological characteristics even further, enabling bearings to function dependably in some applications at speeds higher than 10,000 RPM.
Heavy-Duty Designs for Extreme Loads
Tapered roller bearings must endure high loads in challenging conditions in sectors including mining, construction, and heavy manufacturing. High-speed capability is often subordinated to robustness and contamination resistance in design considerations for these applications. Greater roller complement (full complement designs) and larger roller diameters may significantly boost load capacity; some tapered roller bearings can support dynamic loads of up to 500kN.
It becomes crucial to choose the right material for these demanding applications. Excellent resistance to surface fatigue and wear is provided by through-hardened or case-carburized steels. In order to allow supporting structures to bend without overtaxing the tapered rolling bearing in situations requiring shock loads or misalignment, slightly larger internal clearances may be supplied.
Customization for Specialized Industries
Because of its adaptability, tapered roller bearings may be highly customized to satisfy the particular needs of specialized sectors. For example, weight reduction is crucial in aircraft applications. This might result in the adoption of lightweight, high-strength alloys or hollow rollers, which preserve load capacity while lowering total bearing mass.
The low speed, high load operation and exposure to variable external conditions provide a problem for tapered roller bearings in the renewable energy industry, especially wind turbines. In this case, designers may utilize materials with improved corrosion resistance and unique sealing methods. In order to provide real-time monitoring of crucial factors like temperature, vibration, and load distribution, some sophisticated designs even include sensor systems straight into the bearing assembly.
Conclusion
With their sophisticated geometric design and cutting-edge materials and production processes, tapered rolling bearings are the pinnacle of precision engineering. They are essential in a wide range of applications across many sectors due to their exceptional capacity to manage both radial and axial stresses in a small size. Every component of a tapered roller bearing, from the basic elements of tapered geometry and roller design to more sophisticated features like creative sealing options and material selections, is meticulously tuned for efficiency, performance, and longevity. These bearings will surely change as technology develops further, expanding the realm of what is feasible in mechanical systems and opening up new avenues for industrial capabilities and machine design.
FAQs
1. What are the main advantages of tapered rolling bearings?
Tapered rolling bearings excel in handling combined radial and axial loads, offer high load capacity, and allow for easy assembly due to their separable design.
2. How do tapered roller bearings differ from cylindrical roller bearings?
Unlike Cylindrical roller bearings, tapered roller bearings can handle axial loads in addition to radial loads, thanks to their angled roller geometry.
3. What industries commonly use tapered roller bearings?
These bearings are widely used in automotive, heavy machinery, mining, construction, and precision engineering applications.
Expert Tapered Rolling Bearing Solutions | INNO Bearing
At INNO Bearing, we specialize in designing and manufacturing high-performance tapered rolling bearings for demanding industrial applications. With nearly 30 years of experience, our team of experts can provide customized solutions for your specific needs, from standard sizes up to 5000mm outer diameter. Whether you require precision-engineered bearings for heavy machinery or specialized designs for extreme environments, we have the expertise to deliver. Contact Us at sales@inno-bearing.com to discuss how our tapered roller bearing solutions can enhance your equipment's performance and reliability.
References
1. Smith, J.D. (2019). "Advanced Bearing Technology for Industrial Applications." Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 45(3), 287-301.
2. Johnson, K.L. (2018). "Contact Mechanics in Rolling Element Bearings." Tribology International, 93, 118-127.
3. Zhang, Y., et al. (2020). "Material Innovations in High-Performance Tapered Roller Bearings." Materials Science and Engineering: A, 782, 139271.
4. Brown, M.W. (2017). "Optimization of Tapered Roller Bearing Design for Wind Turbine Applications." Renewable Energy, 112, 330-340.
5. Liu, H., & Chen, W. (2021). "Advanced Sealing Technologies for Tapered Roller Bearings in Harsh Environments." Wear, 477, 203784.
6. Anderson, P.R. (2016). "Precision Manufacturing Techniques for High-Speed Tapered Roller Bearings." Precision Engineering, 46, 168-179.




