The double thrust ball bearing load calculation is an important part of engineering that affects whether machines in many different fields can work properly. These specialized bearings are designed to handle bidirectional axial loads. They need to be carefully tested with math to be sure they work well and last a long time. Correct load calculations keep things from breaking too early, make equipment more efficient, and lower maintenance costs for everything from wind turbines to heavy-duty machinery. Thrust ball bearing load calculations are based on certain ideas that procurement managers and engineers need to know in order to make good choices that keep the business running smoothly while still meeting strict performance standards.
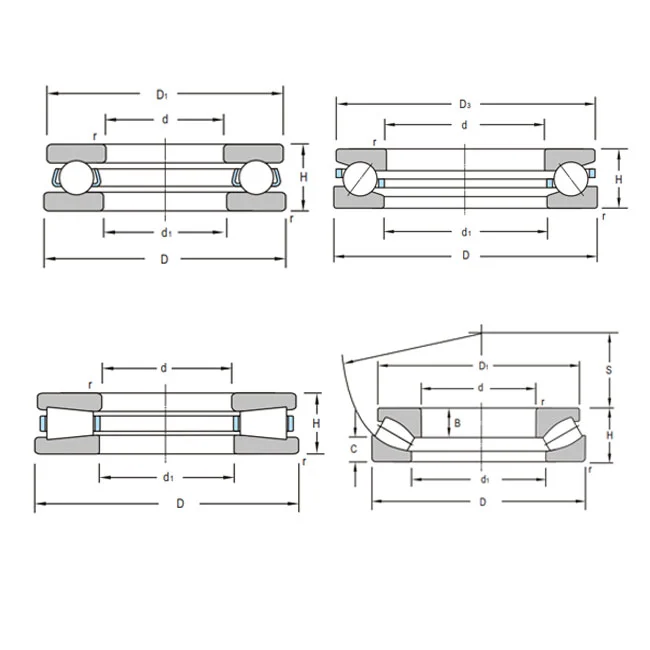
Understanding Double Thrust Ball Bearings and Load Fundamentals
Double Thrust ball bearings have a complex design with an intermediate washer between two shaft washers. This makes a setup that can handle axial loads in both directions at the same time. They can handle loads in both directions, which sets them apart from ones that only handle loads in one direction; those use just one shaft washer and housing washer setup.
Parts of the structure and how the load is spread
The bearing assembly is made up of several important parts that work together to spread axial forces. The main surfaces that hold weight are the shaft washers. They are made of high-quality materials like GCr15, GCr15SIMN, or 20Cr2Ni4A steel. Double-row steel balls with cages made of stamped steel or brass that are precisely designed keep the load even across the bearing assembly. The bearing can handle thrust forces from opposite sides because the middle washer is the main point that load is transferred through.
Classifying Loads and Effect on Performance
Axial loads are the main type of force that double thrust ball bearings are used to manage. However, to make sure that calculations are correct, it is important to understand how different types of loads affect each other. When a load is applied straight, it acts parallel to the bearing's axis of rotation. When a load is applied at an angle, it adds a component that affects the bearing's overall performance. Temperature changes, rotational speeds, and environmental conditions create extra load factors that need to be taken into account by full calculation methods.

Step-by-Step Load Calculation for Double Thrust Ball Bearings
Figuring out the exact operating conditions and load characteristics that affect the double ball thrust bearing assembly is the first step in systematic load calculation. This methodical way guarantees that both the dynamic and static load requirements are correctly measured.
Figuring the Dynamic Load Rating
The dynamic load rating (C) is the steady axial load that a bearing can withstand for one million turns with a 90% chance that it won't break. It uses the basic dynamic load rating that manufacturers provide and changes it based on the speed, temperature, lubrication quality, and other conditions of the operation. Shock loads, misalignment, environmental contamination, and other factors in the real world are taken into account by service factors from 1.2 to 3.0.
Evaluation of Static Load Rating
Static load rating (C0) calculations look at situations where bearings are under load without turning or at very low speeds. This calculation is especially useful for applications that are only used sometimes or that need to stay in place while under load. The static safety factor, which usually falls between 2 and 5, gives enough protection so that the parts of the bearing don't bend out of shape permanently.
Example of a Practical Calculation
Think about a pitch control system for a wind turbine that needs a double thrust ball bearing with an inner diameter of 200 mm and an outer diameter of 300 mm. When the dynamic load calculation is done for something that has to work at 50 RPM with an axial load of 150 kN outdoors, it has to take into account the service factors that include temperature changes and vibrations from the wind. The dynamic load rating needed would be found by multiplying the service factors by the load. This would make sure there are enough safety margins for dependable long-term use.
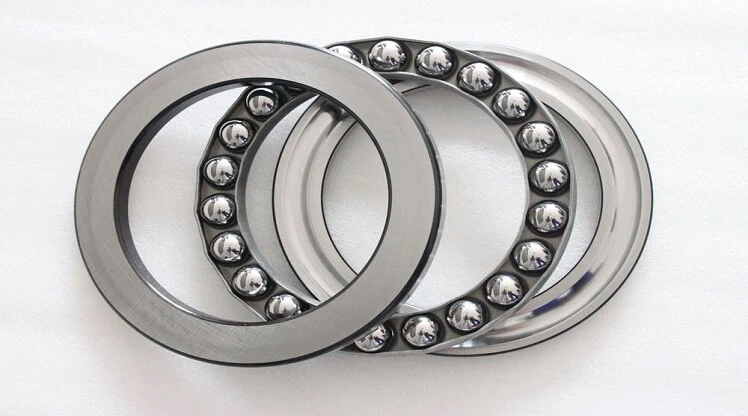

Comparing Double Thrust Ball Bearings with Other Bearings in Load Handling
Knowing the pros and cons of double thrust ball bearings and other types of bearings makes it easier to choose the right one for each job.
Performance Compared to Angular Contact Bearings
Angular contact bearings work best in situations with mixed loads that have both radial and axial forces. On the other hand, double thrust ball bearings work best in situations with only axial loads. Angular contact bearings have a built-in ability to handle radial loads because of their contact angle. This makes them a good choice for machine tool spindles and other situations where mixed loading happens. But, in specialized thrust applications, double thrust ball bearings handle bidirectional axial loads better and have lower friction coefficients.
Thrust Roller Bearing Options
Thrust roller bearings can handle more weight than thrust ball bearings, but they have slower speed limits because of higher friction. Thrust roller bearings can handle heavier axial forces because the line contact between the rollers and the raceways spreads the loads over bigger areas. Because of their point contact geometry, double thrust ball bearings keep their benefits in situations where higher rotational speeds, lower friction, and exact axial positioning are needed.
Maintenance and Procurement Considerations for Load-Optimized Bearings
Keeping the bearing's ideal load capacity during its operational life needs smart buying and maintenance plans that support long-term reliability.
Preventive Maintenance to Keep Load Integrity
Regular inspection protocols focus on checking the space between bearings, the condition of the lubricant, and the way the load is spread out. Vibration analysis can help you find problems before they get really bad, and temperature monitoring can help you find too much friction or not enough lubrication. Proper lubrication keeps the important film between the rolling parts and the raceways. This stops the metal from touching each other, which would quickly lower the load capacity.
Procurement and Supplier Evaluation Tips
Good procurement methods focus on what suppliers can do in areas like precision manufacturing, quality control, and technical support. ISO 9001 and other industry-specific certifications are signs of great manufacturing, and records that show traceability make sure that parts are reliable. Customization options become very important for apps that need non-standard sizes or special materials to meet their specific load needs.

INNO Bearing: Advanced Thrust Ball Bearing Solutions
INNO Bearing's thrust ball bearings are made to exceed the industry's standards for load capacity and operational reliability. That's what the company does best. Many different kinds of products are available from us. They come in single-row and double-row configurations and can handle both unidirectional and bidirectional axial loads in a range of industrial settings.
Technical Information and Customization
The inner diameters of the normal products we sell are between 10mm and 300mm. They're between 30 mm and 400 mm wide and 8 mm and 50 mm tall. Custom Solutions can handle pipes that are up to 5000 mm wide, and they can be made to meet the specific needs of heavy machinery, wind energy, and mining. Along with the standard P0/P6 levels, the precision grades also include P5 high-precision bearings for important uses that need very high levels of accuracy.
Making Sure the Material is High Quality
We use high-quality materials in our manufacturing process to make sure our products can hold a lot of weight and last as long as possible. Some of the materials we use are steels like GCr15, GCr15SIMN, and 20Cr2Ni4A. Advanced heat treatment methods make materials better, while precision grinding gives surfaces the right finish for longer bearing life. Quality control checks the size, material, and performance of each bearing to make sure it meets or exceeds the load ratings.
Conclusion
The key to good industrial equipment design and procurement is to accurately calculate the load for double thrust ball bearings. Engineers and people who work in procurement are able to pick the best bearing solutions for their applications when they know about the relationship between bearing structure, load types, and ways of doing the math. Smart purchasing and proper maintenance help keep a business running smoothly in the long term and lower the total cost of ownership. As industry needs more speed and dependability from its machines, getting good at these math concepts will help people get ahead of others in the job market.
FAQs
How do I find out what the dynamic load rating for my application needs to be?
To get the dynamic load rating, you should multiply your axial load by service factors that are based on how the machine will be used. These include the speed and temperature, shock loads, and bearing life you want. The service factors are most of the time from 1.5 to 3.0. Vibration, misalignment, and lubrication are all things to think about when you choose service factors.
Can double thrust ball bearings handle loads that are both straight on and at an angle at the same time?
For axial loads, double thrust ball bearings are the best choice. However, they are not good for radial loads. Use angular contact bearings or other kinds of bearings made for combined loading situations when there are big radial loads.
When there are high axial loads, what do you do to make sure the bearings keep working for a long time?
Use the right lubricants for the job often, keep an eye on the temperature and vibration levels, make sure everything is correctly mounted and aligned, and do regular checks to look for wear patterns or contamination early on.
Partner with INNO Bearing for Superior Thrust Ball Bearing Solutions
With almost thirty years of experience in engineering and manufacturing, INNO Bearing provides great thrust ball bearing solutions. Our wide range of products meets the tough needs of wind energy, heavy machinery, mining, and industrial equipment with precisely designed bearings that work better than expected. Take advantage of our fast delivery times, extensive customization options, and great technical support that makes sure you choose the right bearings and apply them correctly.
Our experienced engineers offer personalized load calculation consultations to help you meet complicated application needs while improving bearing performance and lowering operational costs. We can be counted on to bring you the right supplies when and where you need them most because we have extensive inventory management and global supply chain capabilities. Get in touch with the specialists at our thrust ball bearing manufacturing company to talk about your needs and learn how our knowledge can help your equipment run better.
Ready to get the most out of your process for choosing bearings? For detailed technical help, custom bearing solutions, and good prices, email us at sales@inno-bearing.com.
References
1. Harris, T.A. & Kotzalas, M.N. "Advanced Concepts of Bearing Technology: Rolling Bearing Analysis, Fifth Edition." CRC Press Engineering Mechanics Series, 2016.
2. International Organization for Standardization. "ISO 281:2007 Rolling Bearings - Dynamic Load Ratings and Rating Life." Geneva: ISO Technical Committee, 2007.
3. Bearing Engineers Association. "Load Calculation Methods for Thrust Ball Bearings in Industrial Applications." Journal of Tribology and Bearing Technology, Vol. 45, 2019.
4. American National Standards Institute. "ANSI/ABMA 11-1990 Load Ratings and Fatigue Life for Ball Bearings." American Bearing Manufacturers Association Standards, 2018.
5. Palmgren, A. "Ball and Roller Bearing Engineering: Fundamentals of Rolling Contact Bearing Design and Analysis." SKF Engineering Handbook Series, Third Edition, 2020.
6. Machine Design Magazine. "Thrust Bearing Selection and Application Guidelines for Heavy Machinery." Industrial Equipment Design Annual, September 2021 Issue.




