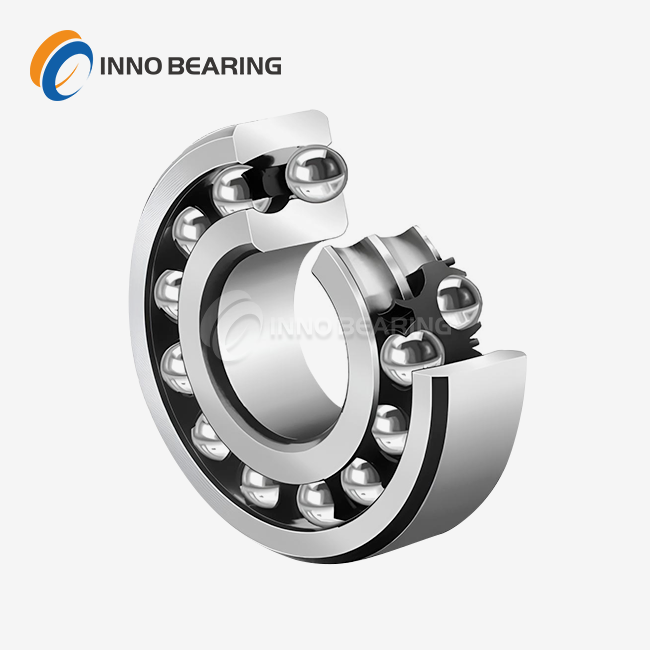
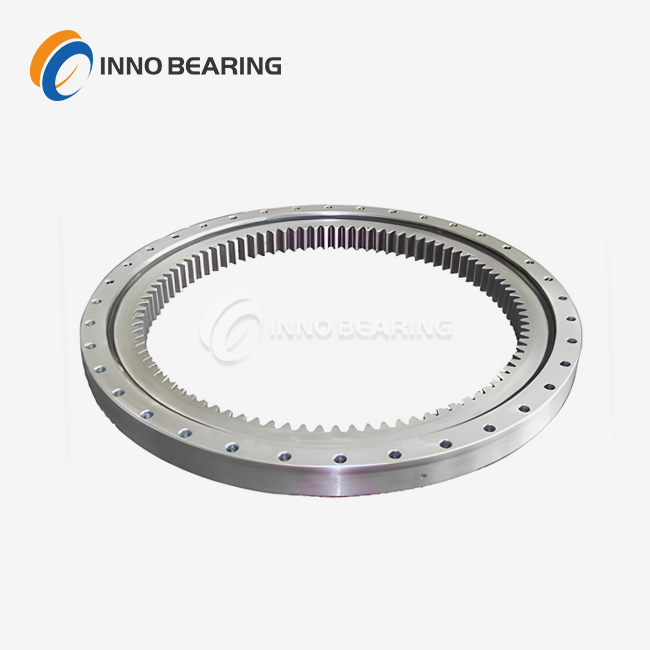
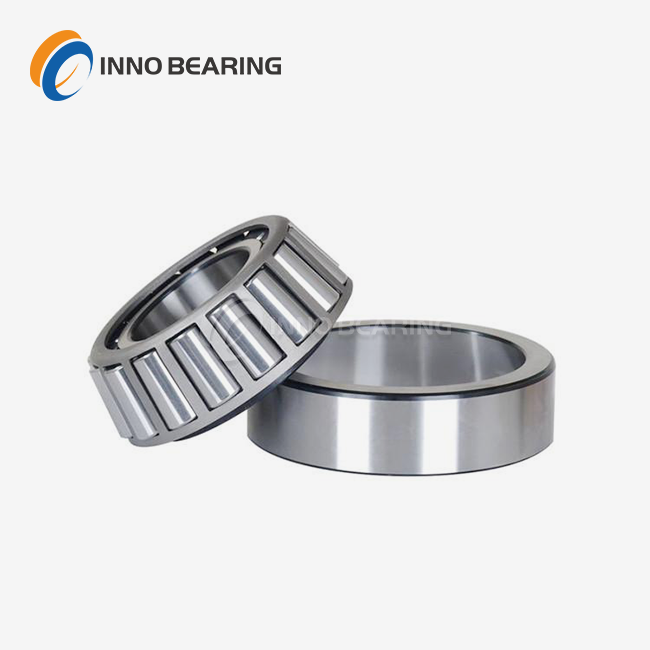
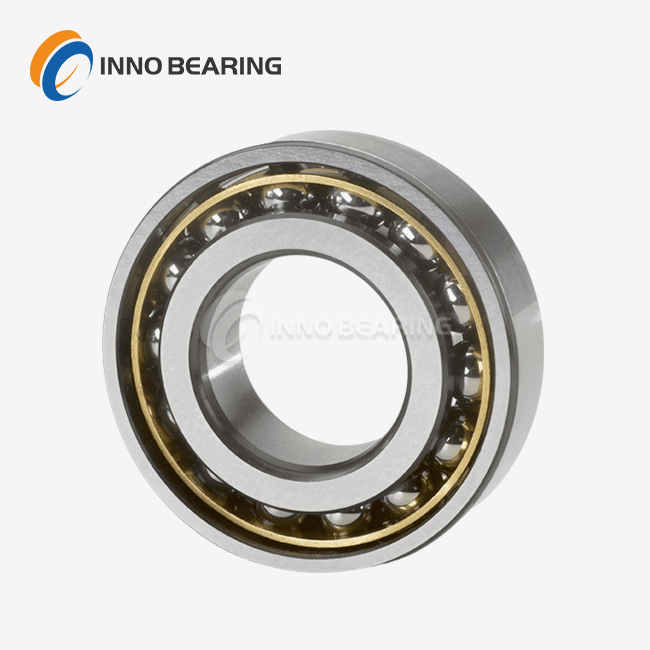
When used in heavy machinery, a slewing ring bearing is a rotational bearing with a large diameter that is specifically designed to support axial, radial, and moment loads while allowing for 360-degree rotation. These critical components consist of inner and outer rings with rolling elements positioned between them, allowing equipment to rotate smoothly under substantial loads. The working principle uses balls or rollers to spread forces across several contact points. The balls or rollers roll along raceways that have been perfectly shaped to reduce friction and wear. Slewing ring bearings are not like regular bearings because they combine many load-handling features into a single, small design. This makes them very important for uses in the wind energy sector to heavy construction equipment where space is limited and load management needs to be top-notch.
Understanding Slewing Ring Bearings: Definition and Structure
Slewing ring bearings are a special type of large bearing that can handle more complicated loads than most other bearing types. These bearings distinguish themselves through their ability to simultaneously accommodate axial forces (parallel to the rotation axis), radial forces (perpendicular to the axis), and tilting moments that occur during operation.
Key Parts of the Structure
The complex engineering behind these bearings can be seen in their basic architecture. The assembly has a number of important parts that work together to make sure it works well. The foundation is made up of a fixed ring and a rotating ring. They are made from strong materials like 50Mn and 42CrMo alloy steels, which are very durable even when conditions are tough.
The rings are connected by rolling elements, which pass on the weight. Balls or rollers are used depending on the needs of the situation. GCr15 bearing steel is the standard material, but GCr15SiMn variants are better at resisting impact in very tough settings. The cage system keeps the rolling parts from hitting each other while making sure there is enough space between them to evenly distribute the weight.
Sealing systems keep the inside parts clean and maintain lubrication. Nitrile rubber seals work fine in most industrial settings. Fluororubber seals work better in very hot settings and ones where oil resistance is important, greatly extending the operational lifetime of the seals.
Size Specifications and Weight Limit
Slew ring bearings made in the last few decades can accommodate a wide range of sizes. The outer ring diameter can be anywhere from 100mm to 4000mm, and the inner ring diameter can be anywhere from 80mm to 3800mm. The heights range from 8 mm to 150 mm. This lets engineers choose the configurations that make the best use of space while still meeting the load requirements. This ability to change dimensions makes it possible for different types of machines to use this part without hurting its performance or structure.

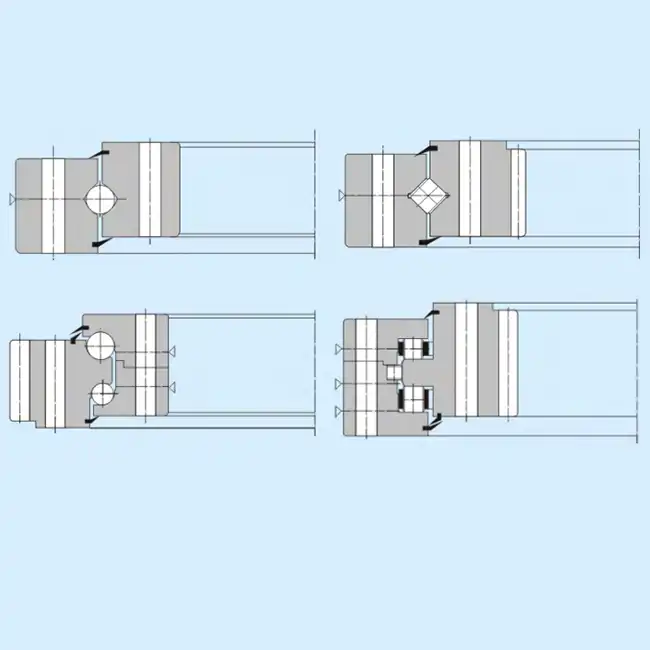
Types and Design Variations of Slewing Ring Bearings
The bearing industry has developed multiple design variants to address specific operational challenges and load characteristics. Understanding these variations enables engineers and procurement professionals to select optimal Solutions for their applications.
Ball-Type Configurations
Single-row ball bearings excel in applications requiring moderate load capacity with cost-effectiveness as a priority. These designs handle axial and radial loads efficiently while maintaining relatively simple manufacturing processes. Double-row ball configurations significantly enhance load-carrying capacity, particularly for moment loads, making them suitable for applications experiencing complex force combinations such as crane turntables and wind turbine yaw systems.
Roller-Type Designs
Crossed roller bearings deliver superior rigidity and precision compared to ball alternatives. The roller arrangement provides increased contact area, distributing loads more effectively across the raceway surfaces. Cylindrical roller variants optimize radial load handling, while tapered configurations excel in applications requiring precise angular positioning.
Selection criteria involve analyzing load magnitude, precision requirements, operational speed, and environmental conditions. Each design variant offers distinct advantages that align with specific operational demands, ensuring optimal performance throughout the bearing's service life.
Core Applications and Industry Use Cases
Slewing Bearings have become necessary in many areas of industry because they make important functions possible in the machines that are the backbone of modern infrastructure and manufacturing.
Wind Power Machines
These bearings are very important in the infrastructure for renewable energy, as shown by wind turbine applications. Yaw systems use slewing bearings with large diameters to point nacelles in the direction of the wind. At the same time, pitch control mechanisms change the angles of the blades so that they can get more energy. These uses require very high fatigue resistance because bearings have to survive millions of cycles with different loading conditions over the course of twenty years.
Building and Heavy Equipment
Slewing ring bearings are used for the main rotation tasks of cranes, excavators, tunnel boring machines, and other heavy equipment. These bearings can be used in many different ways, and crane applications show this best. They support the rotation of the boom while also lifting very heavy loads and dealing with the forces that happen when materials are moved. Being able to add gear teeth directly to the bearing rings makes drive systems simpler and lowers the overall complexity of the equipment.
Ship loaders, offshore cranes, and other port machinery put bearings in harsh marine environments that need special treatments to resist corrosion and better sealing systems. These tough conditions have led to new materials and protective coatings that make the service life much longer.

Maintenance, Lifespan, and Performance Optimization
To maximise bearing life, keep them lubricated, dirt-free, and monitored.
Lubrication Management
The key to bearing longevity is proper lubrication. Grease selection depends on temperatures, loads, and environment. Standard lithium-based greases are fine for industrial use. Synthetic lubricants work better in extreme heat or cold. Heavy-duty machines need more frequent lubrication.
Quality and performance monitoring
Dimensional accuracy, slewing flexibility, and rolling element noise are critical inspection parameters. Modern quality control protocols use high-tech testing tools before use. These rigorous testing methods ensure that bearings meet strict usage standards.
Predictive maintenance detects issues early with vibration and temperature monitoring. This preventative measure reduces unplanned downtime and speeds replacements. This saves a lot throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Comparison and Procurement Insights for B2B Clients
Selecting slewing bearings requires careful consideration of technical and commercial factors that affect long-term operational success.
Tech Specification Alignment
Maximum operational forces and safety factors must be considered when calculating load ratings. Corrosive environments require special treatments or materials. Some applications require ultra-precise positioning, while others value load capacity over accuracy.
Criteria for Supplier Evaluation
Manufacturing capabilities, quality certifications, and technical support distinguish bearing suppliers in the competitive market. Applications requiring non-standard dimensions or features need customisation. Delivery reliability affects project schedules, so supplier logistics is crucial.
Beyond purchase price, total cost of ownership includes maintenance, service life, and replacement complexity. Premium bearings often offer better value due to lower lifecycle costs.
INNO Bearing: Your Trusted Slewing Ring Bearing Manufacturer
INNO Bearing is a leading manufacturer of precision bearings for demanding industrial applications with nearly 30 years of experience. We offer R&D, design optimisation, manufacturing excellence, and technical service support.
Manufacturing Excellence and QA
In addition to repair and import substitution, our advanced production facilities can customise large and non-standard bearings up to 5000mm diameter. Advanced testing equipment ensures every bearing meets quality standards before delivery, and our quality control systems maintain 99.9% defect-free production.
Advanced manufacturing processes and strict quality protocols produce bearings with high dimensional accuracy, load capacity, and operational life. Our engineers work closely with clients to create customised application solutions.
Industry-Specific Options
We offer specialised bearing solutions for various industries. Metallurgical applications use high-temperature resistant materials and protective coatings, while wind energy applications use fatigue-resistant designs for multi-decade service. Port machinery solutions have marine-grade corrosion protection and sealing systems.
From design to installation to maintenance, technical support is available throughout the product lifecycle. This comprehensive approach optimises bearing performance and minimises operational disruptions.

Conclusion
Slewing ring bearings are very important parts that make it possible for modern heavy machinery to work in a wide range of settings. Engineers and procurement professionals can make smart choices that boost equipment performance and operational efficiency when they know the working principles, design variations, and application requirements of the tools they use. These bearings will do their job reliably for as long as they're supposed to, thanks to the right choice, quality production and good maintenance. Slew bearings will remain a key part of helping technology move forward and increasing productivity in industry as machines get more complicated and need to function better.
FAQs
How do I calculate slewing ring bearing load capacity?
Calculate the maximum axial, radial, and moment loads your equipment will experience during operation and apply safety factors to determine load capacity. Dynamic loading, operational cycles, and environmental factors may affect bearing performance over its service life.
How often should heavy-duty slewing ring bearings be maintained?
Operational intensity, environment, and load characteristics determine maintenance intervals. Visual inspections should be done monthly, and lubrication should be done every 6–2 years depending on application severity. Continuous monitoring systems can optimise maintenance scheduling for critical applications.
Are slewing ring bearings customisable for special machinery?
Reputable manufacturers offer non-standard dimensions, specialised materials, integrated gear teeth, and improved sealing systems. Custom solutions can meet performance standards while addressing unique load requirements, environmental issues, and space constraints.
Partner with INNO Bearing for Superior Slewing Ring Bearing Solutions
Global engineering teams trust INNO Bearing to deliver precision-engineered slewing ring bearings that exceed performance expectations in the most demanding applications. Our three decades of manufacturing experience and cutting-edge production capabilities ensure your equipment works reliably in harsh conditions.
Our technical experts support you from design consultation to operational optimisation for standard or custom configurations. At every stage of production, our global logistics network ensures fast delivery and high quality.
Take advantage of our proven track record serving leading manufacturers across wind energy, heavy machinery, mining, and port infrastructure sectors. Contact our engineering team today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how INNO Bearing can enhance your equipment's performance and reliability. Reach out to our technical experts at sales@inno-bearing.com to begin your partnership with a trusted slewing ring bearing supplier committed to your operational success.
References
Harris, T.A. and Kotzalas, M.N. "Essential Concepts of Bearing Technology: Rolling Bearing Analysis, Fifth Edition." CRC Press, 2006.
Tedric, A. Harris. "Rolling Bearing Analysis: Advanced Concepts of Bearing Technology." John Wiley & Sons, 2001.
International Organization for Standardization. "Rolling bearings - Slewing rings - Part 1: Dimensions and tolerances." ISO 12043-1:2007.
American Bearing Manufacturers Association. "Load Ratings and Fatigue Life for Ball Bearings." ABMA Standard 9-1990.
Warda, B. and Chudzik, A. "Fatigue Life Prediction of the Radial Roller Bearing with the Waviness Error." Applied Sciences, 2020.
Schaeffler Technologies AG & Co. "Rolling Bearings: Technical Handbook for Industrial Applications." 2019 Edition.




