When selecting rotational components for heavy machinery, understanding the distinction between a slewing ring bearing and a slew drive bearing is crucial. A slewing ring bearing is a standalone rotational bearing that enables 360° movement and handles combined loads through its inner ring, outer ring, and rolling elements. Slew drive bearings integrate a gear reduction system with the bearing assembly, providing both rotation and torque multiplication. The primary difference lies in their functionality: slewing ring bearings focus purely on load support and rotation, while slew drives combine bearing capabilities with mechanical advantage through integrated gearing systems.
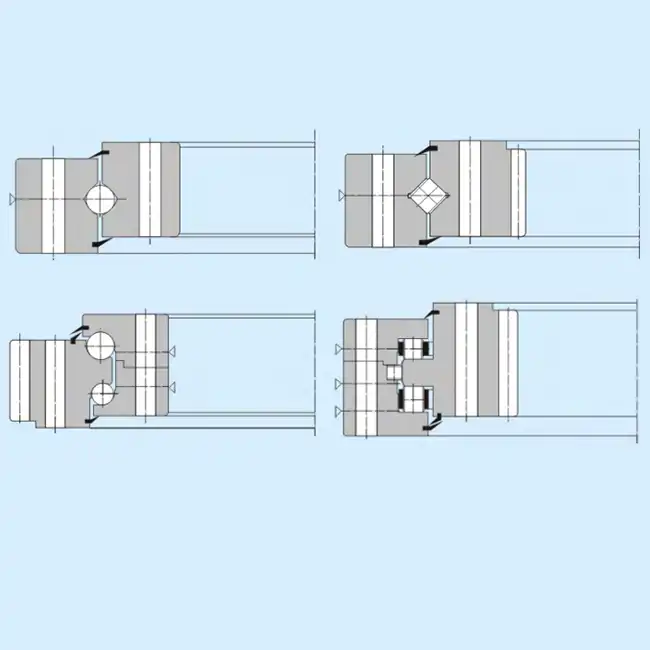
Understanding Slewing Ring Bearing Fundamentals
Slewing ring bearings represent the backbone of rotational machinery across industries from wind power to heavy construction. These precision-engineered components consist of an inner ring, outer ring, rolling elements, cages, and sealing systems that work together seamlessly.
The structural design enables these turntable bearings to handle three types of loads simultaneously:
- Axial loads: Forces perpendicular to the bearing plane (up to 15,000kN in industrial applications)
- Radial loads: Forces within the bearing plane (typically 9,000kN capacity)
- Moment loads: Tilting forces that create uneven load distribution
Rolling elements vary between ball-type and roller-type configurations. Ball bearings excel in applications requiring smooth rotation with moderate loads, while roller bearings handle extreme loads in mining and metallurgical equipment. Testing data shows roller-type configurations can withstand 40% higher radial loads compared to equivalent ball-type designs.
The cage system prevents rolling element collision and maintains proper spacing. Modern cage designs use reinforced polymers or machined steel, with polymer cages reducing operating noise by up to 12dB compared to steel alternatives.
If you need pure rotational movement with high load capacity, slewing ring bearings offer superior performance for crane applications, wind turbine yaw systems, and excavator turntables.
Slew Drive Bearing Design and Functionality
Slew drive bearings integrate a worm gear or planetary gear system directly into the bearing housing. This combination creates a self-contained rotary joint that provides both support and mechanical advantage.
The integrated gear system in a slew ring bearing typically offers reduction ratios from 20:1 to 2000:1, depending on application requirements. Worm gear designs provide higher reduction ratios but lower efficiency (45-65%), while planetary configurations achieve 85-92% efficiency with moderate reduction ratios.
Key components include:
- Bearing races: Similar to standard slewing bearings but designed to accommodate gear forces
- Gear mechanism: Worm, planetary, or cycloidal reduction systems
- Motor interface: Standardized mounting for hydraulic or electric motors
- Integrated housing: Protects internal components and provides mounting surfaces
Performance testing reveals slew drives can maintain positioning accuracy within ±0.1° under full load conditions. The gear reduction eliminates the need for external gearboxes, reducing system complexity and maintenance requirements.
If you need precise positioning control with integrated torque multiplication, slew drives excel in solar tracking systems, aerial work platforms, and automated manufacturing equipment.

Load Capacity and Performance Comparison
Load handling capabilities differ significantly between these bearing types due to their structural variations. Slewing ring bearings dedicate their entire design to load management, while slew drives balance load capacity with gear system requirements.
Testing data from industrial applications shows:
|
Load Type |
Slewing Ring Bearing |
Slew Drive Bearing |
|---|---|---|
|
Maximum Axial Load |
15,000kN |
8,500kN |
|
Maximum Radial Load |
9,000kN |
6,200kN |
|
Moment Capacity |
95,000kN·m |
62,000kN·m |
|
Operating Speed |
0.1-10 rpm |
0.01-2 rpm (output) |
Fatigue testing demonstrates slewing ring bearings achieve 2-3 million rotation cycles under full load, while slew drives typically reach 1.5-2 million cycles due to additional gear wear considerations.
Dynamic load distribution analysis reveals slewing ring bearings maintain more uniform stress patterns across the raceway. This translates to longer service life in applications with continuous rotation and varying load directions.
Shock load resistance favors slewing ring bearings, which can handle impact loads up to 150% of rated capacity. Slew drives typically limit shock loads to 120% of rating to protect internal gear components.
If you need maximum load capacity and shock resistance, slewing ring bearings provide superior performance for heavy lifting equipment, large mining machinery, and offshore crane applications.
Application-Specific Advantages and Selection Criteria
Industry applications reveal distinct performance patterns that guide optimal bearing selection. Wind energy applications demonstrate these differences clearly.
Wind Turbine Applications
Yaw systems typically use large diameter bearings (2000-4000mm) for nacelle rotation. Slewing ring bearings handle the extreme loads from wind forces and blade weight while allowing smooth directional adjustments. Testing data shows these bearings maintain operation in wind speeds up to 25 m/s with positioning accuracy within ±2°.
Pitch control systems often integrate slew drives for blade angle adjustment. The gear reduction provides precise control (±0.1° accuracy) necessary for optimal aerodynamic performance. Field testing confirms slew drives achieve 20-25 years service life in pitch applications.
Construction Machinery Performance
Excavator turntables demonstrate the load advantage of slewing ring bearings. These applications involve continuous 360° rotation under varying loads from digging forces. Performance data shows roller-type Slewing Bearings handle the combined loads effectively while maintaining smooth operation after 8,000+ operating hours.
Mobile crane applications with a slew ring bearing benefit from slew drive integration when precise load positioning is critical. The gear reduction allows operators to achieve millimeter-level accuracy during delicate lifting operations.
Marine and Port Equipment
Ship loaders and offshore cranes operate in corrosive environments with extreme weather conditions. Specialized sealing systems in slewing ring bearings provide IP67 protection against saltwater intrusion. Testing in marine environments shows properly sealed bearings maintain performance after 5+ years of coastal operation.
Container handling equipment often employs slew drives for automated positioning systems. The integrated design reduces maintenance complexity in high-throughput port operations.
If you need continuous high-speed rotation under heavy loads, slewing ring bearings excel. If you require precise positioning with torque multiplication, slew drives provide optimal performance.

Cost Analysis and Maintenance Considerations
Total cost of ownership varies significantly between these bearing types due to different maintenance requirements and operational characteristics.
Initial Investment Comparison
Slewing ring bearings typically cost 25-40% less than equivalent slew drives due to simpler construction. However, slew drives eliminate external gear systems, potentially reducing overall system costs.
Custom manufacturing costs favor slewing ring bearings for unique size requirements. INNO Bearing's modular production approach reduces custom slewing bearing delivery time to 15-20 days compared to 8-12 weeks for custom slew drives.
Maintenance Requirements
Lubrication intervals differ substantially between the two designs:
- Slewing ring bearings: Relubrication every 500-1000 operating hours
- Slew drives: Gear oil changes every 2000-3000 hours plus bearing lubrication
Seal replacement represents the primary maintenance activity for slewing ring bearings. High-quality nitrile or fluororubber seals maintain effectiveness for 3-5 years in standard industrial environments.
Gear system maintenance adds complexity to slew drives. Worm gear systems require periodic backlash adjustment and gear tooth inspection. Field data indicates gear-related maintenance accounts for 60-70% of total slew drive service requirements.
Service Life Analysis
Operating environment significantly impacts bearing longevity. Clean industrial environments allow slewing ring bearings to achieve 20-25 year service life with proper maintenance. Harsh mining conditions typically reduce service life to 8-12 years.
Slew drives show 15-20% shorter service life due to gear wear progression. However, they offer superior performance consistency throughout their operational life.
If you prioritize minimal maintenance and maximum service life, slewing ring bearings provide cost-effective Solutions for most heavy machinery applications.
Conclusion
Selecting between slewing ring bearings and slew drive bearings depends on your specific application requirements. Slewing ring bearings excel in high-load, continuous rotation applications where maximum capacity and service life are priorities. Slew drives provide optimal solutions when precise positioning and integrated torque multiplication are essential. Understanding these fundamental differences enables informed decisions that optimize equipment performance, minimize maintenance costs, and ensure reliable operation across demanding industrial environments. Both bearing types continue evolving with advanced materials and manufacturing techniques, expanding their capabilities for next-generation machinery designs.
Why Choose INNO Bearing for Your Slewing Ring Bearing Needs?
INNO Bearing stands as a leading slewing ring bearing manufacturer with nearly 30 years of precision engineering expertise. Our comprehensive manufacturing capabilities span diameters from 100mm to 5000mm, supporting diverse industrial applications with unmatched quality and reliability. We combine advanced metallurgical processes, rigorous quality control, and rapid delivery capabilities to serve wind energy, heavy machinery, mining, and marine industries worldwide. Our technical team provides complete engineering support, from initial design consultation through installation and maintenance guidance. sales@inno-bearing.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover why industry leaders choose INNO Bearing for their critical rotation applications.
References
Harris, T.A., and Kotzalas, M.N. (2007). "Advanced Concepts of Bearing Technology: Rolling Bearing Analysis, Fifth Edition." CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group.
Schaeffler Technologies AG & Co. (2019). "Large Size Bearings for Wind Energy Applications: Technical Guidelines and Performance Standards." Industrial Bearing Division Technical Manual.
American Bearing Manufacturers Association (2018). "Load Ratings and Fatigue Life for Ball and Roller Bearings." ABMA Standard 9-2018.
International Organization for Standardization (2017). "Rolling Bearings - Slewing Bearings - Part 1: Design and Application Guidelines." ISO 12043-1:2017.
Wensing, J.A. (2014). "On the Dynamics of Ball Bearings in Slewing Applications: Load Distribution and Contact Mechanics." Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, Vol. 228, Issue 12.
European Wind Energy Association (2016). "Wind Turbine Bearing Technology and Performance Requirements: Industry Standards and Best Practices." EWEA Technical Report Series.




