To measure and fit a conical roller bearing properly, you need to know the exact dimensions, use the right methods for installation, and have a system for making sure everything is correct. These tapered bearings will only work well in heavy-duty machinery if the hole diameter, outer diameter, width, and preload settings are all taken into account. Professional installation uses calibrated micrometers, keeps strict cleanliness standards, and follows manufacturer-specified torque values during assembly to avoid failure before time and maximize operating lifespan.
Understanding Conical Roller Bearings: Core Concepts Before Measurement and Fitting
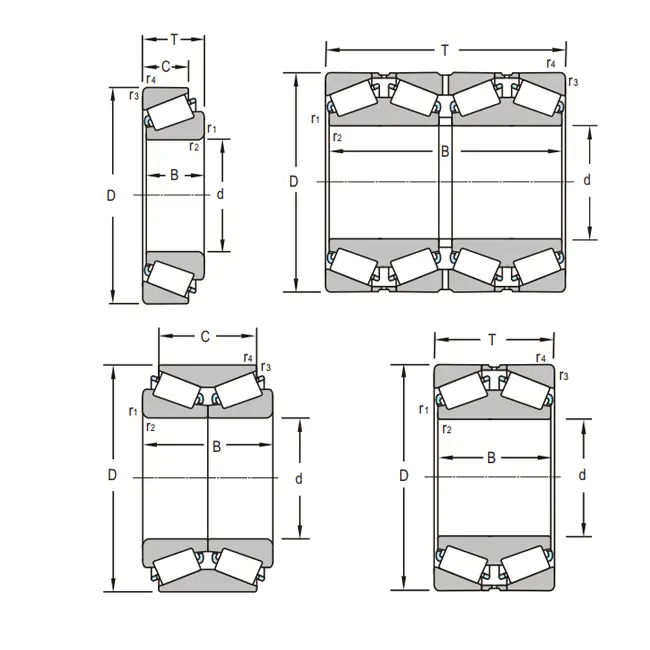
Conical roller bearings are a complex engineering invention that can handle both radial and axial loads thanks to the carefully thought-out shape of their rollers and raceways. This makes them more durable and better at spreading out the load. Their cone-shaped rollers and carefully machined raceways let them work well under heavy loads and at high speeds. They often work better than other kinds of bearings in these situations. It's important to know the main design and practical benefits, such as being able to handle misalignment and working better under very high stresses, before doing any measurements or fitting.
What Is a Conical Roller Bearing and How Does It Work?
A conical roller bearing has an inner ring with a tapered raceway and an outer ring that can be either a separable single-row or a set double-row design. It also has precision rollers and cages. The basic working principle depends on the geometric arrangement of tapered surfaces. Cone-shaped rollers spread loads over the best contact areas. With heavy-duty use, this design lets the bearing handle both horizontal and axial forces at the same time, with a load capacity of up to 3,500 kN. The tapered shape makes a wedging action that automatically centers the bearing while it's working. This gives it great stability even when the load changes. GCr15 or GCr15SiMn steel is often used for rings and rollers. Stamped steel or brass cages make sure that the rollers are spaced correctly and the oil can do its job.
Common Applications and Key Benefits in Industrial Use
Heavy and fast situations in many industries show that Tapered Roller Bearings can be used in a lot of different kinds of tough situations. Wind energy applications gain from being able to handle extreme axial forces in turbine main shafts and yaw systems. At the same time, construction machinery depends on their strength for excavator swing mechanisms and crane rotation systems. The mining industry values that especially in conveyor systems and grinding mills, they are resistant to pollution and shock loads.
Key benefits are better load distribution, a longer service life even in tough circumstances, and great tolerance of shaft misalignment. These bearings work consistently well at temperatures ranging from −60°C to +500°C. This makes them a good choice for both Arctic wind sites and steel mills. Conical designs have 40% more load capacity than regular ball bearings while keeping the same level of precision as the P0/P6 standard or P5/P4 for very high-precision uses.
Preparing for Accurate Measurement: Key Dimensions and Tools
To make sure that conical roller bearings fit and work well in mechanical systems, you need to measure accurately first. Bore diameter, outer diameter, bearing width, and cone height are all critical measurements that have a direct effect on the way bearing parts and mating surfaces connect with each other. Precise measurement of axial clearance and preload settings is necessary because these factors directly affect the bearing's lifespan and its ability to function under different load conditions.
Essential Dimensions to Measure for Proper Bearing Fit
Primary dimensional measures include bore diameters from 10 mm to 1,000 mm in standard setups. Custom Solutions for specialized uses can go up to 5,000 mm. The outer diameter must be between 26 mm and 2000 mm. The width usually falls between 8 mm and 300 mm, based on the load and how it needs to be installed. For the right setup settings, it's very important to accurately measure the height of the cone. For the best performance, the measurement has to be within 0.002 mm. The axial clearance change has a direct effect on how long bearings last. Typical values fall between 0.05 mm and 0.25 mm, depending on the conditions in which the bearing is working and the effect of thermal expansion. Engineers can choose the right bearing types that match the needs of certain applications when they understand these dimensional relationships. This also keeps the design margins for safety and reliability.
Recommended Tools and Techniques for Precise Measurement
Professionals use tools that are properly calibrated. These tools include digital micrometers that can measure as precisely as 0.001 mm, dial indicators that help figure out how much something moves in a straight line, and specialized bearing fitting tools that are made for setups with large diameters. For very important uses, coordinate measuring machines (CMM) check all of the dimensions, and for installations that need to be exactly right, laser interferometry gives the highest level of precision.
In the first step of the measurement process, the parts are brought to a normal temperature of 20°C. This is followed by a check of the overall dimensions at a number of points along the circumference to look for possible changes in shape. Profilometers are used to measure surface roughness and make sure that the finish quality is good enough for the grease film to form. Writing down all of the measurements and making sure they can be traced back to national standards helps make sure quality standards are met and makes it easier to fix things when performance problems come up.
Avoiding Common Measurement Mistakes That Compromise Bearing Performance
Keeping the temperature wrong while measuring dimensions often causes mistakes. This is because objects can expand or contract with the temperature, which changes the measurements and affects the estimates of how well the parts will fit. Ignoring the specifications for angular contact can lead to improper preload settings. Also, not taking into account housing thermal growth during working conditions may lead to too much interference fits. Errors from pollution in the measurement processes spread through the installation steps, which can lead to bearing failure before the end of its expected lifetime. Wearing gloves that don't leave lint, keeping your workspace clean, and using the right tools for lifting heavy bearings are all proper handling techniques that will keep the bearings from changing shape while you measure them.

Step-by-Step Guide to Fitting a Conical Roller Bearing Correctly
Proper fitting of conical roller bearings follows a systematic, multi-step process beginning with thorough preparation and culminating in comprehensive verification testing. The installation sequence demands meticulous attention to cleanliness, precise dimensional control, and systematic verification at each stage to ensure reliable operation throughout the bearing's service life.
Preparing the Shaft and Housing for Installation
Comprehensive cleaning and inspection of shaft and housing components establishes the foundation for successful bearing installation. Surface preparation involves removing all traces of previous lubricants, corrosion products, and debris using appropriate solvents and cleaning techniques that preserve surface integrity. Visual inspection identifies potential defects including scratches, nicks, or dimensional irregularities that could compromise bearing performance.
Tolerance verification ensures proper fit characteristics between bearing and mating components, with typical shaft tolerances ranging from h6 to k6 depending on load and speed requirements. Housing bore tolerances generally fall within H7 to M7 ranges, providing appropriate interference or clearance fits based on operational demands. Surface finish requirements typically specify Ra values between 0.8 and 3.2 micrometers for adequate lubrication retention and load distribution.
Methods of Fitting: Press Fit, Heat Fit, and Adjusting Clearance
Installation method selection depends on conical roller bearing size, interference requirements, and available equipment capabilities. Thermal expansion fitting proves particularly effective for large bearings, utilizing controlled heating to 80-100°C to achieve thermal growth sufficient for easy installation without mechanical stress. Oil bath heating or induction heating systems provide uniform temperature distribution while preventing overheating damage to bearing materials.
Press-fitting techniques require specialized tooling designed to apply force evenly across bearing races, avoiding point loading that could cause component damage. Hydraulic fitting tools offer precise force control with real-time monitoring capabilities, ensuring installation forces remain within manufacturer specifications. Cold fitting methods may be appropriate for smaller bearings with minimal interference requirements, utilizing mechanical pullers or threaded installation tools.
Setting and Adjusting Preload and Axial Clearance
Preload adjustment directly influences bearing operational characteristics including stiffness, load distribution, and fatigue life. Proper preload eliminates internal clearance while avoiding excessive stress that could reduce bearing longevity. Measurement techniques include dial indicator monitoring during installation torque application, with typical preload values ranging from 10-50 microns displacement depending on bearing size and application requirements.
Axial clearance verification ensures adequate space for thermal expansion while maintaining proper load distribution across roller elements. Temperature considerations account for differential expansion between shaft, housing, and bearing materials during operation, with clearance adjustments compensating for these thermal effects to maintain optimal preload throughout operating temperature ranges.
Testing and Verification Post-Installation
Initial operation verification includes comprehensive checks for smooth rotation, appropriate operating temperatures, and absence of unusual noise or vibration signatures. Baseline measurements establish reference values for future monitoring, including vibration amplitude, frequency spectra, and thermal profiles under normal operating conditions. Break-in procedures typically involve gradual load application with careful monitoring of operating parameters to ensure proper bedding of contact surfaces and lubrication distribution.
Maintenance Tips and Lifespan Optimization for Conical Roller Bearings
Systematic maintenance programs maximize bearing performance and service life through proactive monitoring and preventive interventions. Regular maintenance schedules adapted to specific operating conditions help identify potential issues before they develop into costly failures, supporting operational continuity and equipment reliability.
Routine Inspection and Lubrication Best Practices
Lubrication management forms the cornerstone of bearing maintenance, with selection criteria based on operating temperatures, speeds, and environmental conditions. Synthetic lubricants offer superior performance in extreme temperature applications, while mineral-based options provide cost-effective solutions for standard operating conditions. Relubrication intervals typically range from 500 to 5000 operating hours depending on application severity and environmental factors.
Visual inspection protocols identify early warning signs including discoloration, unusual wear patterns, or contamination evidence that could indicate developing problems. Vibration analysis using accelerometers and spectrum analyzers provides quantitative assessment of bearing condition, with trending analysis revealing gradual deterioration patterns that enable predictive maintenance scheduling.
Troubleshooting Common Issues: Noise, Vibration, and Premature Failure
Diagnostic procedures systematically address performance anomalies through root cause analysis and corrective action implementation. Excessive noise often indicates lubrication deficiency, contamination presence, or improper preload settings requiring immediate attention. Vibration analysis reveals specific failure modes including roller defects, raceway damage, or cage instability, each requiring targeted corrective measures. Temperature monitoring identifies thermal issues related to inadequate lubrication, excessive preload, or bearing overload conditions that threaten operational reliability and component longevity.

Where to Source High-Quality Conical Roller Bearings and Related Services?
Supplier selection significantly impacts bearing performance, reliability, and total cost of ownership throughout equipment operational life. Reputable manufacturers combine advanced metallurgy, precision manufacturing, and comprehensive quality assurance to deliver products meeting demanding industrial requirements.
Selecting Reliable Suppliers and Manufacturers
SKF, NSK, Timken, FAG, KOYO, and other global companies set standards for quality based on decades of work in engineering and manufacturing. These well-known names offer a wide range of products, helpful technical support, and service networks that can meet a variety of needs. Specialized manufacturers that focus on custom solutions are one other sourcing choice. These manufacturers often give their customers the chance to be more competitive in certain market segments or application niches.
Manufacturers in China have shown big improvements in quality while still being able to compete on price, especially for large or non-standard conical roller bearing setups. ISO certification compliance, quality management systems implementation, and technical skill assessment through facility audits and product testing are all ways of judging something.
Procurement Considerations: MOQ, Lead Time, and Custom Solutions
Procurement strategies find a balance between lowering costs and making sure that supplies are always on hand. This is done by carefully looking at things like minimum order amounts, delivery schedules, and what suppliers are capable of. Agreements to buy in bulk often make things much cheaper and make sure that there is enough inventory on hand to meet upkeep needs. When it comes to big or custom bearings, lead time is very important because it can take anywhere from a few weeks to a few months to make them. The time it takes to make something depends on how complicated it is and how much capacity the supplier has.
Certification standards that include performance tests, reports on dimensions, and material traceability help meet the goals of regulatory compliance and quality assurance. After-sales support includes things like professional help, warranty coverage, and field service that add value after the product has been delivered.
How INNO Bearing Supports Your Conical Roller Bearing Needs?
Luoyang INNO Bearing Co., Ltd. uses almost 30 years of experience in making to provide precisely designed solutions for difficult industrial applications. Our wide-ranging skills include custom bearing design up to φ5000mm, unique ways of treating heat, and strict quality control methods that make sure consistent performance in a range of conditions.
Application analysis, custom design optimization, and help with field installation are all engineering support services that maximize bearing performance and minimize total cost of ownership. Advanced testing facilities make sure that the design specs and operating reliability are correct by doing fatigue testing, vibration analysis, and thermal performance assessment. Quality assurance methods include performance testing, dimensional verification, and material traceability. These steps help meet strict industry standards and customer needs.
Conclusion
Systematic focus on dimensional correctness, proper installation methods, and thorough checking processes are needed to successfully measure and fit conical roller bearings. Using the right tools to measure, the right ways to fit, and the right tests to check them will make sure that bearings work well for a long time. Quality parts from trustworthy sources and professional fitting help keep equipment running smoothly and cut down on downtime. Engineering teams can get the same results in a lot of different areas of industry as long as they know these basic ideas. This helps the business run smoothly and lets them keep things working without spending too much money.
FAQs
How do I know if the conical roller bearing is fitted correctly?
Verify correct preload through dial indicator measurement, ensure smooth rotation without excessive noise or heat generation, and confirm consistent axial clearance measurements around the bearing circumference. Proper fitting typically results in operating temperatures within 40°C of ambient during normal operation.
What are the most common causes of conical roller bearing failure during installation?
Installation failures typically result from inadequate dimensional measurement, improper fitting techniques that cause component damage, contamination during assembly, or insufficient lubrication application. Temperature control during installation and proper handling procedures prevent most installation-related problems.
Can I interchange conical roller bearings with tapered roller bearings?
While these terms often describe similar bearing designs, specific dimensional characteristics, load ratings, and performance specifications vary between manufacturers and applications. Proper engineering analysis ensures compatibility and optimal performance for specific application requirements.
Partner with INNO Bearing for Superior Conical Roller Bearing Solutions
INNO Bearing delivers precision-engineered tapered roller bearings designed for extreme industrial environments, combining advanced metallurgy with customization capabilities up to φ5000mm. Our comprehensive quality assurance processes and rapid delivery schedules support critical maintenance requirements while our engineering team provides application-specific optimization recommendations. As a trusted conical roller bearing manufacturer, we maintain extensive inventory levels and offer competitive pricing structures that optimize procurement efficiency. Contact Us at sales@inno-bearing.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our solutions enhance equipment reliability while reducing total cost of ownership across demanding applications.
References
Harris, T.A., and Kotzalas, M.N. "Essential Concepts of Bearing Technology: Rolling Bearing Analysis, Fifth Edition." CRC Press, 2007.
Palmgren, A. "Ball and Roller Bearing Engineering, Third Edition." SKF Industries Inc., 1959.
Hamrock, B.J., Schmid, S.R., and Jacobson, B.O. "Fundamentals of Fluid Film Lubrication, Second Edition." Marcel Dekker Inc., 2004.
ISO 281:2007. "Rolling bearings - Dynamic load ratings and rating life." International Organization for Standardization.
Tallian, T.E. "Failure Atlas for Hertz Contact Machine Elements, Second Edition." ASME Press, 1999.
Eschmann, P., Hasbargen, L., and Weigand, K. "Ball and Roller Bearings: Theory, Design and Application, Second Edition." John Wiley & Sons, 1985.




